Deploy Azure Load Balancer using Terraform
Overview
Azure Load Balancer is used for distributing load (incoming traffic) to multiple resources hosting the same application. This ensures high availability of the application as the Load Balancers distributes traffic to healthy resources.
There are two types of Azure Load Balancers:
- Public Load Balancer.
- Private or Internal Load Balancer.
Public Load Balancer has public IP address as its frontend and is used for load balancing traffic sourcing from internet. An Internal Load Balancer has private IP address as its frontend and is used for load balancing traffic to internal applications from private networks.
In this blog, we will deploy an Azure Load Balancer for distributing traffic to two Azure Virtual Machines hosting a simple Nginx web service using Terraform.
Please note that this blog assumes that you know how to deploy of Azure Load Balancers using Azure Portal and you have an Azure Subscription.
Prerequisites
Please install Azure CLI and Terraform for deploying Azure resources.
Deploy a Public Load Balancer
In this section, we will deploy a Public Load Balancer with Backend Pool consisting of two Azure Virtual Machines. These VMs will host a simple web page configured by using a custom script extension for Nginx web service. We will perform complete deployment using Terraform.
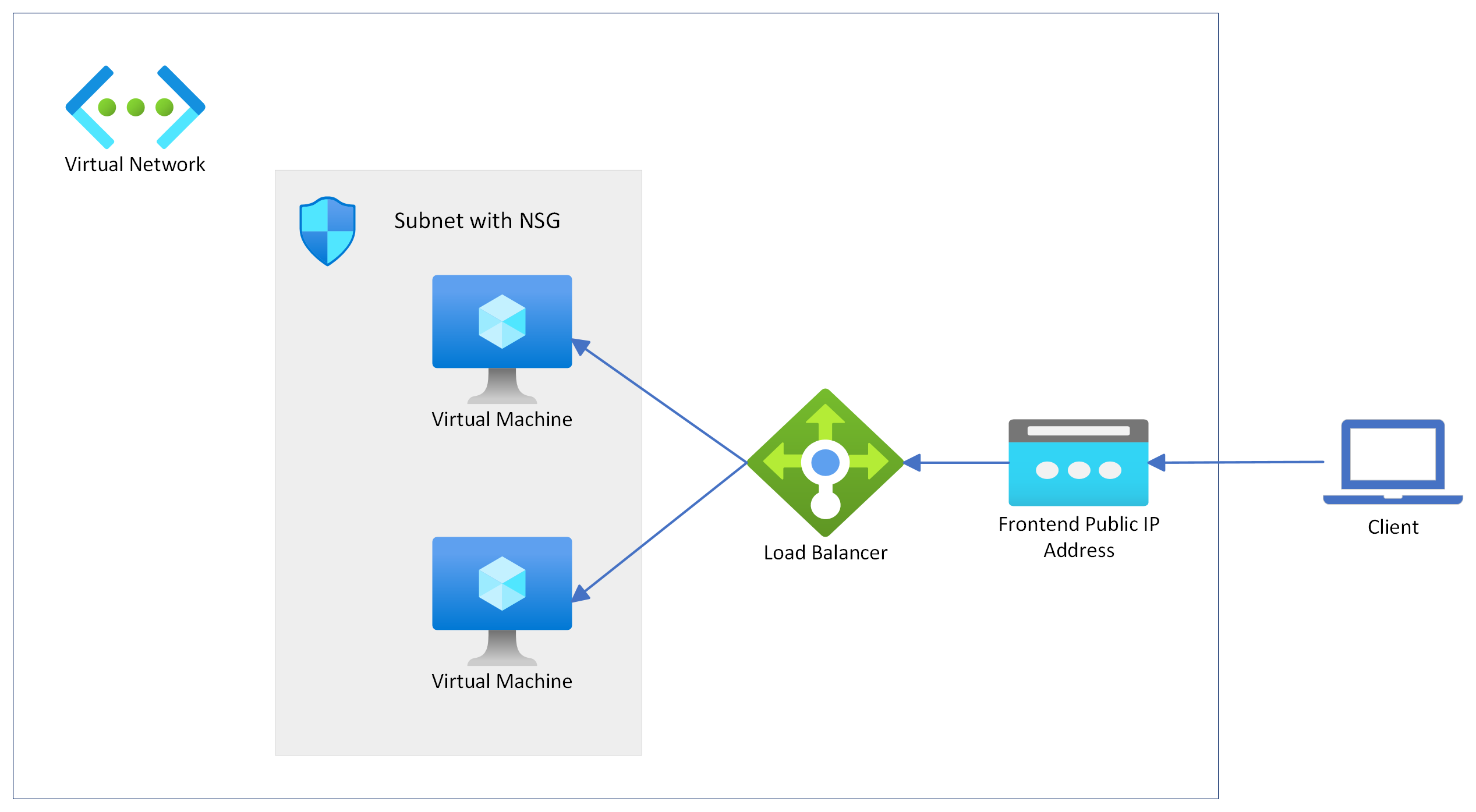
Public Load Balancer Lab Setup
This is how our architecture will look after the deployment is completed.
Create and Deploy Terraform script
-
Create a directory and make it as your current directory.
mkdir load-balancer-demo cd load-balancer-demo -
Create a file named
providers.tfand paste the configuration below. Here we have configuredazurermas Terraform provider for creating and managing our Azure resources. -
Create a file named
variables.tfand paste the configuration below. We declare all the variables that we intend to use in our Terraform deployment in thevariables.tffile. You could modify the default values as per your choice or naming convention for Azure resources. -
Create a file named
main.tfand paste the configuration below. Themain.tfis our configuration file where we use to deploy our Azure resources. -
Create a file named
outputs.tfand paste the configuration below. This is display the IP address in URL format which we could use for accessing our application. -
Initialize the working directory containing Terraform configuration files (
load-balancer-demoin our case).terraform init -upgrade -
Create an execution plan to preview the Terraform deployment.
terraform plan -out main.tfplan -
Apply Terraform configuration previewed in the execution plan.
terraform apply main.tfplan
Verify the deployment
When you apply the execution plan, Terraform displays the frontend public IP address. If you’ve cleared the screen, you can retrieve that value with the following Terraform command:
echo $(terraform output -raw public_ip_address)
You could verify if you could access our web page by using the frontend Public IP address of the Azure Load Balancer.
Deploy an Internal Load Balancer
This time we will deploy an Internal Load Balancer. Since the frontend IP address of an Internal Load Balancer is private IP address, we will also deploy another Virtual Machine from where we could access the web page hosted in the backend pool VMs using the frontend IP address of an Internal Load Balancer.
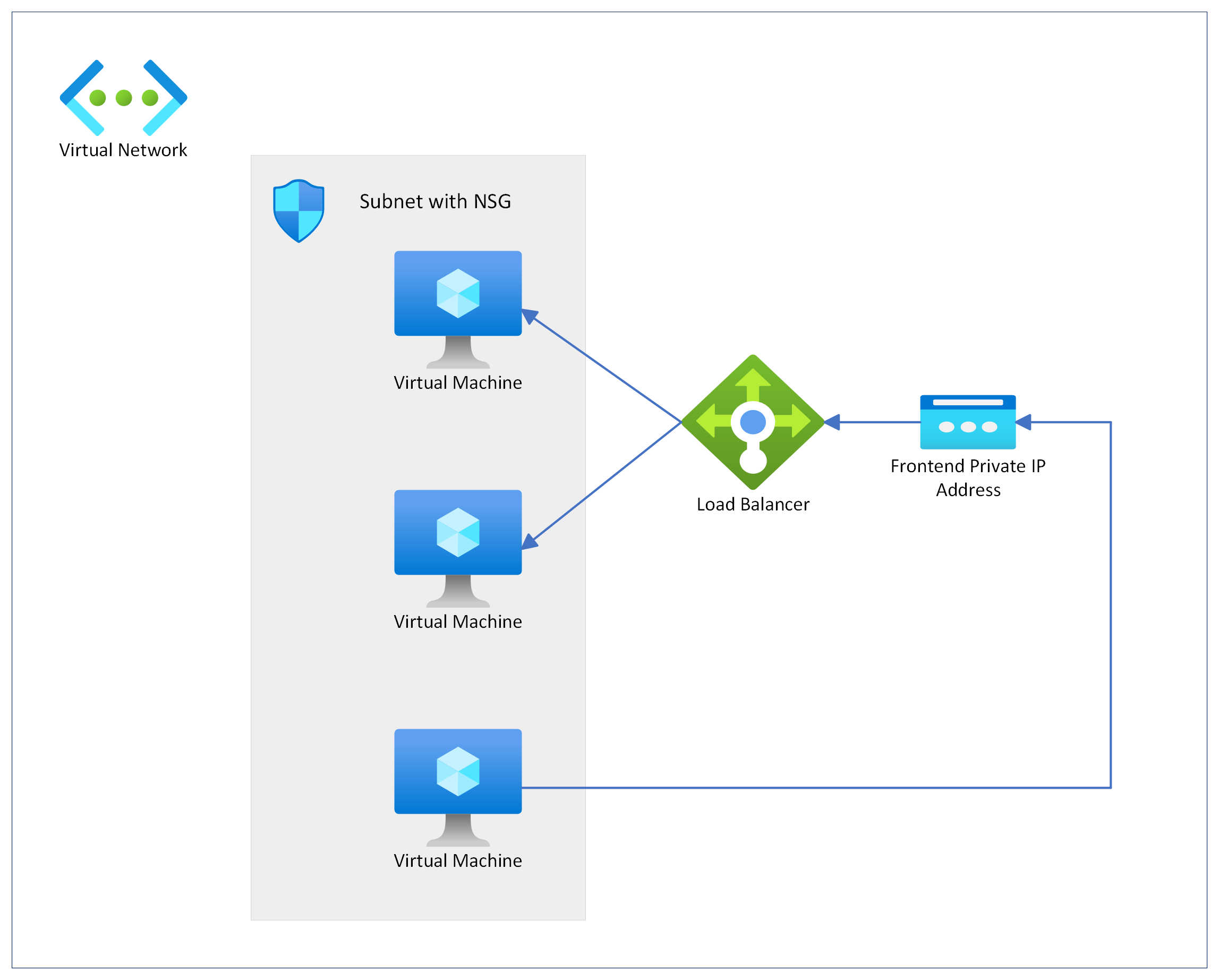
Internal Load Balancer Lab Setup
This is how our architecture will look after the deployment is completed.
Create and Deploy Terraform script
-
Create a directory and make it as your current directory.
mkdir internal-load-balancer-demo cd internal-load-balancer-demo -
Create a file named
providers.tfand paste the configuration below. Here we have configuredazurermas Terraform provider for creating and managing our Azure resources. -
Create a file named
variables.tfand paste the configuration below. We declare all the variables that we intend to use in our Terraform deployment in thevariables.tffile. You could modify the default values as per your choice or naming convention for Azure resources. -
Create a file named
main.tfand paste the configuration below. Themain.tfis our configuration file where we use to deploy our Azure resources. -
Create a file named
outputs.tfand paste the configuration below. This is display the IP address in URL format which we could use for accessing our application. -
Initialize the working directory containing Terraform configuration files (
internal-load-balancer-demoin our case).terraform init -upgrade -
Create an execution plan to preview the Terraform deployment.
terraform plan -out main.tfplan -
Apply Terraform configuration previewed in the execution plan.
terraform apply main.tfplan
Verify the deployment
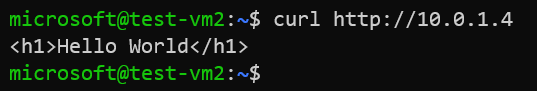
Since frontend IP of an Internal Load Balancer is private IP, you cannot connect to it from internet. Connect to the VM which is not a backend pool member using SSH and verify if you could access our web page using the private IP displayed in the output bash apply command.
Delete the resources
In order to avoid any extra charges, it is advisable to delete the resources which are not required. You could delete all the Azure resouces which we have deployed so far using Azure Portal or by executing the following Terraform commands.
terraform plan -destroy -out main.destroy.tfplan
terraform apply main.destroy.tfplan
Please note that the above commands need to be executed in the working directory containing Terraform configuration files (internal-load-balancer-demo in our case).