Deploy a Linux VM in Azure with initial configuration using cloud-init script
Overview
We could deploy VMs in Azure using images available in Azure Marketplace.
If we want to perform custom configuration then we would need to create a custom image and deploy using that custom image from Azure Compute Gallery. This allows us to deploy multiple VMs using the same custom image ensuring same configuration exists in all deployed VMs.
we cloud also perform some initial configuration by executing a script while deploying the VM using cloud-init. The cloud-init configuration is executed in the initial boot of the Azure VM.
In this blog, we will deploy an Azure Linux VM with initial configuration using cloud-init. Our initial configuration will be running a Docker continer for static web content using Nginx.
Pre-requisites
You must have an active Azure subscription for following through the steps in this blog.
Create the cloud-init script
We would create cloud config file named cloud-config.yml file with contents below.
#cloud-config
package_reboot_if_required: true
package_update: true
package_upgrade: true
packages:
- curl
- ca-certificates
- moby-engine
- moby-cli
write_files:
- path: /run/scripts/example.conf
content: |
server {
listen 8080;
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://www.example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 8443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/bundle.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/server.key;
server_name www.example.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/nginx.vhost.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/nginx.vhost.error.log;
root /var/www/www.example.com;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
}
permissions: '0755'
- path: /run/scripts/example.dockerfile
content: |
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update && apt-get -y install nginx openssl curl ca-certificates
RUN openssl ecparam -out root.key -name prime256v1 -genkey
RUN openssl req -new -sha256 -key root.key -out root.csr -subj "/C=IN/ST=TL/L=HYD/O=myOrg/OU=IT/CN=example.com/emailAddress=hostmaster@example.com"
RUN openssl x509 -req -sha256 -days 365 -in root.csr -signkey root.key -out root.crt
RUN openssl ecparam -out server.key -name prime256v1 -genkey
RUN openssl req -new -sha256 -key server.key -out server.csr -subj "/C=IN/ST=TL/L=HYD/O=myOrg/OU=IT/CN=www.example.com/emailAddress=hostmaster@example.com"
RUN openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA root.crt -CAkey root.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -days 365 -sha256
RUN cat server.crt >> bundle.crt && cat root.crt >> bundle.crt
RUN mkdir -p /etc/ssl/private
RUN mkdir -p /etc/ssl/certs
RUN mv server.key /etc/ssl/private/server.key
RUN mv bundle.crt /etc/ssl/certs/bundle.crt
RUN mkdir -p /var/www/www.example.com
RUN touch /var/www/www.example.com/index.html
RUN echo '<h1>Hello World!</h1>' >> /var/www/www.example.com/index.html
RUN touch /var/log/nginx/nginx.vhost.access.log
RUN touch /var/log/nginx/nginx.vhost.error.log
COPY example.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.conf
EXPOSE 8080 8443
STOPSIGNAL SIGQUIT
ENTRYPOINT ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
permissions: '0755'
runcmd:
- sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dports 80,443 -j ACCEPT
- sudo iptables-save > /etc/systemd/scripts/ip4save
- sudo systemctl restart iptables.service
- sudo systemctl enable docker
- sudo systemctl start docker
- docker build -t exampleimage -f /run/scripts/example.dockerfile /run/scripts
- docker run -d -p 80:8080 -p 443:8443 --name examplecontainer exampleimage
The cloud config file dictates the inital configuration performed using cloud-init during the first time boot process of the Azure VM.
The cloud config file is in YAML format consisting several modules for verious aspects of the configuration. The first line of the cloud config is always #cloud-config for ensuring that the file is identified by cloud-init and is processed as intended.
The following module of the cloud config file updates from the repository and installed all the upgradable packages in the VM after which the packages listed will be installed. We could also specify the package manager to be used to install the packages and add additional repository using this module.
package_reboot_if_required: true
package_update: true
package_upgrade: true
packages:
- curl
- ca-certificates
- moby-engine
- moby-cli
In the write_files module of our cloud config file, we will create example.conf and example.dockerfile for the Nginx configuration and Docker File for running a container. This module enables us to specify the absolute path and permissions of the file.
write_files:
- path: path/to/file
content: |
#Add the contents of a file in plain text
permissions: '0755'
We will specify execution of required commands in the module runcmd.
runcmd:
- sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dports 80,443 -j ACCEPT
- sudo iptables-save > /etc/systemd/scripts/ip4save
- sudo systemctl restart iptables.service
- sudo systemctl enable docker
- sudo systemctl start docker
- docker build -t exampleimage -f /run/scripts/example.dockerfile /run/scripts
- docker run -d -p 80:8080 -p 443:8443 --name examplecontainer exampleimage
The cloud-init comes with a rich list of modules for configuration.
Deploy Azure Linux with cloud-init using Azure CLI
We will deploy an Azure Linux VM using Azure CLI.
- Login to Azure.
az login
- Create a Resource Group.
az group create --name "testgrp" --location "centralindia"
- Create a public IP for the Azure VM.
az network public-ip create --name "testip" --resource-group "testgrp" --location "centralindia" --allocation-method "Static" --sku "Standard" --tier "Regional"
- Create an Application Security Group. We will be associating our VM’ NIC to this ASG later.
az network asg create --name "testasg" --resource-group "testgrp" --location "centralindia"
- Create NSG with rule to allow traffic on ports 80 and 443 to the ASG and associate it to the VM subnet. The ASG will be associated to the NIC, thus, allowing traffic to the VM.
az network nsg create --name "testnsg" --resource-group "testgrp" --location "centralindia"
az network nsg rule create --name "inboundwebtraffic" --nsg-name "testnsg" --resource-group "testgrp" --priority 800 --direction "Inbound" --access "Allow" --source-address-prefixes "Internet" --source-port-ranges "*" --destination-asgs "testasg" --destination-port-ranges 80 443 --protocol "Tcp"
- Create VNet with a subnet.
az network vnet create --name "testvnet" --resource-group "testgrp" --location "centralindia" --address-prefixes "192.168.100.0/24" --subnet-name "vmsubnet" --subnet-prefixes "192.168.100.0/29" --network-security-group "testnsg"
- Create a NIC associating it to the ASG and public IP created in the previous steps.
az network nic create --name "testnic" --resource-group "testgrp" --location "centralindia" --subnet "vmsubnet" --application-security-groups "testasg" --ip-forwarding "false" --private-ip-address "192.168.100.4" --subnet "vmsubnet" --vnet-name "testvnet" --public-ip-address "testip"
- Create the Azure Linux VM. Our cloud config file will be passed on using the flag
--custom-dataof az vm create command.
az vm create --name "testvm" --resource-group "testgrp" --location "centralindia" --image "MicrosoftCBLMariner:cbl-mariner:cbl-mariner-2:latest" --size "Standard_B2s_v2" --security-type "Standard" --nics "testnic" --nic-delete-option "Delete" --os-disk-delete-option "Delete" --authentication-type "password" --admin-username "username" --admin-password "password" --custom-data "cloud-config.yml"
Verifying the cloud-init configuration
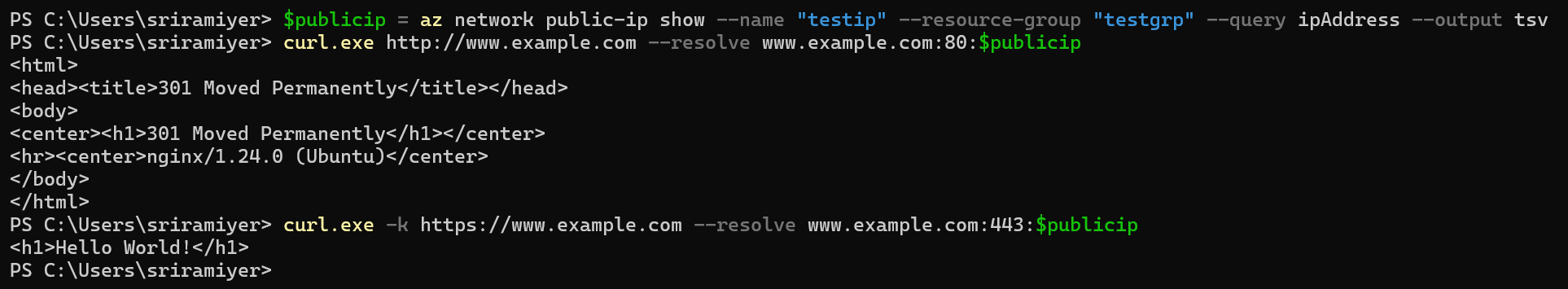
We could verify if the cloud-init configuration was successfull by checking if we could get response from Nginx container in the VM using curl utility.
$publicip = az network public-ip show --name "testip" --resource-group "testgrp" --query ipAddress --output tsv
curl.exe http://www.example.com --resolve www.example.com:80:$publicip
curl.exe -k https://www.example.com --resolve www.example.com:443:$publicip
publicip=$(az network public-ip show --name "testip" --resource-group "testgrp" --query ipAddress --output tsv)
curl http://www.example.com --resolve www.example.com:80:$publicip
curl -k https://www.example.com --resolve www.example.com:443:$publicip
Example:
We could debug any issues in cloud-init configuration of Azure VM by following this public guidance from Azure.